Reproduce bug: Remote Code Execution in Melis Platform
Continuing from the previous article series, in this post, I will apply the knowledge learned and research on PHP deserialize to reproduce CVE-2022-39298
- There is currently no POC code available on this internet for this CVE, but there is a blog post discussing it: Remote Code Execution in Melis Platform | Sonar (sonarsource.com)
- This blog is based on the blog Remote Code Execution in Melis Platform | Sonar (sonarsource.com) and will be written in my own understanding.
I Building environment
-
What is melis-framework?
Melis Framework is an open-source PHP web application framework for building custom, modular, and scalable e-commerce solutions. It is based on the Laminas Framework (formerly known as the Zend Framework) and provides additional modules and tools to make it easier to develop e-commerce applications.
Melis Framework features a powerful and flexible content management system, which allows developers to create custom pages, blocks, and widgets. It also includes a robust shopping cart system with support for multiple payment gateways, shipping providers, and tax rates. Additionally, it offers various integrations such as social media, mailing list services, and Google Analytics.
Melis Framework uses the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture and relies on the Composer dependency management system to manage packages and libraries. It is highly customizable and extensible, allowing developers to add their own modules, themes, and plugins to meet specific project requirements.
One of the most challenging issues I find when reproducing this CVE related to this framework is having to rebuild the environment, which takes a considerable amount of time and effort.
After spending a few days searching for many sources of information on the internet (in fact, there are not many resources discussing this issue), I found that the best way is to follow the step-by-step video instructions on the website Download & Documentation (melistechnology.com. However, there is a difficulty that the website only provides installation instructions for the next step on the Windows platform, while I am using it on the Linux environment.
I noticed that there was a section in the guide for building docker-compose. Therefore, I decided to read the contents the docker-compose.yml file, make some modifications to build it locally.
The important notice here is that during setup, at the final step, it is advisable to follow the video tutorial to create a sample site. This helps us save time in triggering the vulnerability.
II Vulnerability identification
-
At
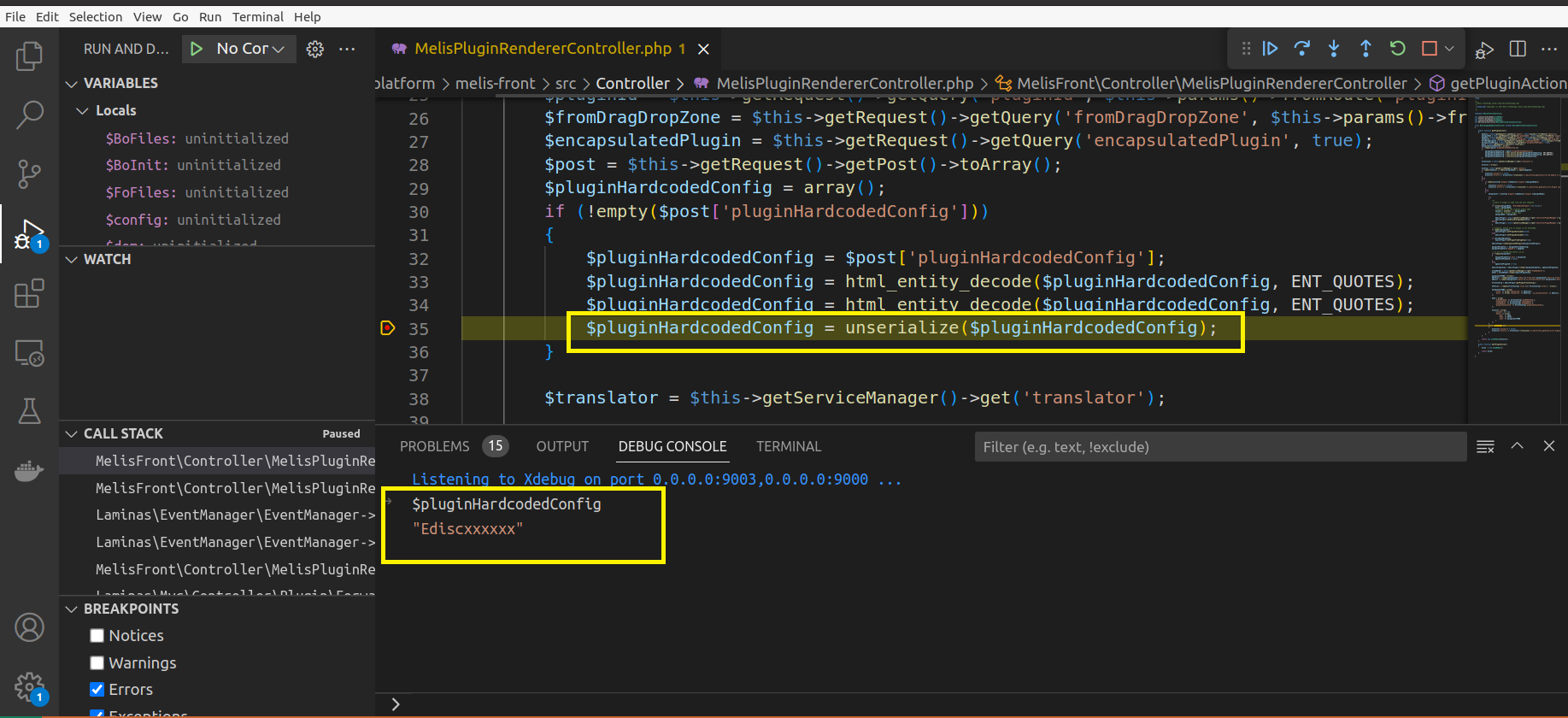
melis-front/src/Controller/MelisPluginRendererController.php1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13class MelisPluginRendererController extends MelisAbstractActionController { public function getPluginAction() { // [...] $post = $this->getRequest()->getPost()->toArray(); // [1] $pluginHardcodedConfig = array(); if (!empty($post['pluginHardcodedConfig'])) { $pluginHardcodedConfig = $post['pluginHardcodedConfig']; // [2] $pluginHardcodedConfig = html_entity_decode($pluginHardcodedConfig, ENT_QUOTES); $pluginHardcodedConfig = html_entity_decode($pluginHardcodedConfig, ENT_QUOTES); $pluginHardcodedConfig = unserialize($pluginHardcodedConfig); // [3] -
At line 13, the
unserialize()function is called with the parameter$pluginHardcodedConfigwhich is obtained from$post(at line 6). -
The class
MelisPluginRendererControlleris extended fromMelisAbstractActionControllerclass which is located inLaminas\Mvc\Controller\AbstractActionController. -
From this, we can infer the framework being used is Lamimas. The
Laminas\Mvc\Controller::getRequest()method returns an object of typeLaminas\Http\Request. This object has agetPost()->toArray()method which retrieves the POST data and stores it in$post(at line 6). An attacker can control the value of this variable.
III Finding source from sink
-
Tracing the sink, I found that it is related to the file
module.config.phpin melis-platform. -
The source code of
vendor/melisplatform/melis-front/src/Controller/MelisPluginRendererController.phpshows that:- This bug relates to a plugin.
- This Framework is built following the MVC model.
-
trên trang document của melis, có 1 trang webdemo
-
On the Melis documentation page, there is a web demo and a sample config page.
-
From here, I realize that the vulnerability occurred on the website hosted on the Melis framework, but what I am doing is looking for the bug on the Melis framework, which is the wrong direction. 😔😔😔
Therefore, the next step is to create a website hosted on the Melis-framework like the sample site on the local machine.
-
After a day of research, I found out the cause of the issue. During the installation process, there was an option to install with a demo version. After installing, all I need to do is access the demo website, and the plugin will automatically trigger.
|
|
And at this point, we can also control any value passed into the unserialize() function, which is enough to move on to the next phase.
IV Building a POP chain
-
There is a paper discussing this exploitation technique.
Supporting tool - PHPGGC
PHPGGC is a library of unserialize() payloads along with a tool to generate them, from command line or programmatically. When encountering an unserialize on a website you don’t have the code of, or simply when trying to build an exploit, this tool allows you to generate the payload without having to go through the tedious steps of finding gadgets and combining them. It can be seen as the equivalent of frohoff’s ysoserial, but for PHP. Currently, the tool supports gadget chains such as: CodeIgniter4, Doctrine, Drupal7, Guzzle, Laravel, Magento, Monolog, Phalcon, Podio, Slim, SwiftMailer, Symfony, Wordpress, Yii and ZendFramework.
- link: https://github.com/ambionics/phpggc
- PHPGCC includes a chain that allows deleting any file.
|
|
But the impact causes is too too significant and destructive for organizations. As a pentester, we need to find other chains that have less impact.
Finding new chain
- The author’s experience with unserialize shows that the caching systems are suitable targets for attacks and control. Because most applications tend to trust the content from the cache.
- The application uses
laminas/laminas-cacheas a third-party dependency, which supports various backend storage features such asapcu,blackhole,mongodb,filesystem,memcached,memory,redisandsession. - After going through the classes, the author found a comment in the code
|
|
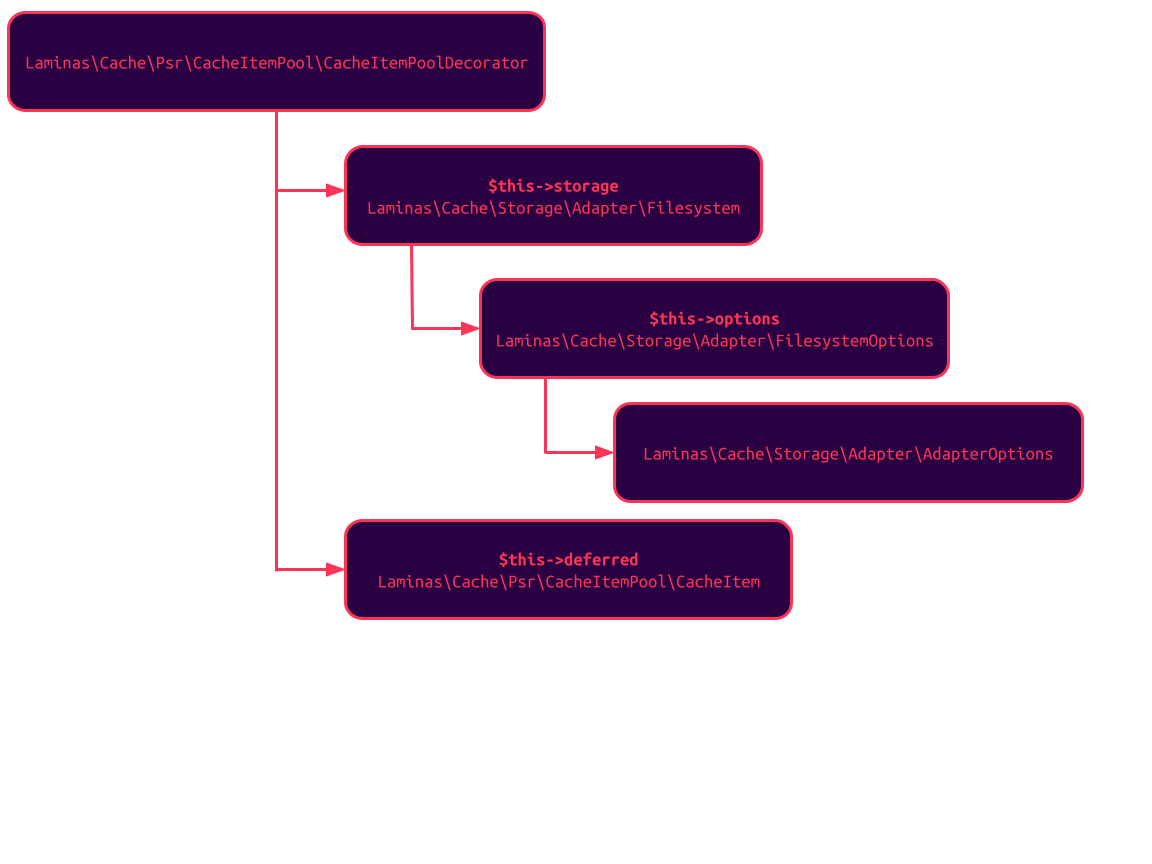
At laminas-cache/src/Psr/CacheItemPool/CacheItemPoolDecorator.php
|
|
-
This means that there must be some way to use this class to store new items in the cache.
-
Go deeper into the
commit()function atvendor/laminas/laminas-cache/src/Psr/CacheItemPool/CacheItemPoolDecorator.php1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13public function commit() { $notSaved = []; foreach ($this->deferred as &$item) { if (! $this->save($item)) { $notSaved[] = $item; } } $this->deferred = $notSaved; return empty($this->deferred); }- It is easy to notice that all values of
$this->deferredare saved to cache by the$this->save()function (lines 5-9)
- It is easy to notice that all values of
-
Go deeper into the
$this->save()function1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41public function save(CacheItemInterface $item) { if (! $item instanceof CacheItem) { throw new InvalidArgumentException('$item must be an instance of ' . CacheItem::class); } $itemTtl = $item->getTtl(); // delete expired item if ($itemTtl < 0) { $this->deleteItem($item->getKey()); $item->setIsHit(false); // không có trong cache return false; } $saved = true; $options = $this->storage->getOptions(); $ttl = $options->getTtl(); try { // get item value and serialize, if required $value = $item->get(); // reset TTL on adapter, if required if ($itemTtl > 0) { $options->setTtl($itemTtl); } $saved = $this->storage->setItem($item->getKey(), $value); // saved items are a hit? see integration test CachePoolTest::testIsHit() $item->setIsHit($saved); } catch (Exception\InvalidArgumentException $e) { throw new InvalidArgumentException($e->getMessage(), $e->getCode(), $e); } catch (Exception\ExceptionInterface $e) { $saved = false; } finally { $options->setTtl($ttl); } return $saved; }-
The code line
$saved = $this->storage->setItem($item->getKey(), $value);is used to save the value to the filesystem storage backend, and since we can control all variables of deserialized classes, we can point the filesystem storage to any file on the local disk and write to it. -
Điều này có thể bị khai thác bằng cách tạo một kịch bản PHP trên đĩa, có thể được thực thi trực tiếp bởi trình thông dịch. Miễn là tập lệnh có phần mở rộng
.phpvà bắt đầu bằng<?php, bất kỳ dữ liệu nào trước nó đều bị bỏ qua và trình thông dịch PHP sẽ thực thi tập lệnh. -
This can be exploited by creating a PHP script on disk that can be directly executed by the interpreter. As long as the script has
.phpextension and starts with<?php, any data before it will be ignored, and the PHP interpreter will execute the script.
-
-
Workflow (from Remote Code Execution in Melis Platform | Sonar (sonarsource.com))
My Exploit
This is the code I’ve written to exploit this vulnerability
|
|